Blockchain Technology - How It Works & Why It Matters
Blockchain technology is the backbone of cryptocurrencies, providing security, transparency, and decentralization. But how does it actually work? In this guide, we’ll break down blockchain step by step, explaining its key components, how transactions are processed, and its real-world applications.
What is Blockchain?
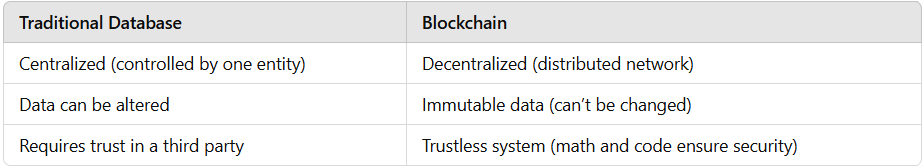
A blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. Unlike traditional databases, blockchains are decentralized, meaning no single authority controls them.
Key Features of Blockchain:
✔
Decentralized
– No single entity owns or controls it.
✔
Immutable
– Once recorded, data cannot be altered.
✔
Transparent
– Transactions are visible to all participants.
✔
Secure – Uses cryptography to prevent fraud.
💡 Example: Bitcoin’s blockchain records every Bitcoin transaction ever made.
How Does a Blockchain Work?
A blockchain consists of blocks linked together in a chain. Each block contains:
🔹
Transaction Data
– Details of the transactions.
🔹
A Timestamp
– When the block was created.
🔹
A Unique Hash
– A cryptographic code identifying the block.
🔹
The Hash of the Previous Block
– Linking it to the previous block.
🔗 Step-by-Step Process:
1️⃣ A transaction is created (e.g., Alice sends Bitcoin to Bob).
2️⃣ The transaction is broadcast to a network of computers (nodes).
3️⃣ The transaction is verified by nodes using a consensus mechanism (e.g., Proof of Work).
4️⃣ Verified transactions are grouped into a block.
5️⃣ The block is added to the blockchain, making the transaction permanent.
Types of Blockchains
Not all blockchains work the same way. There are three main types:
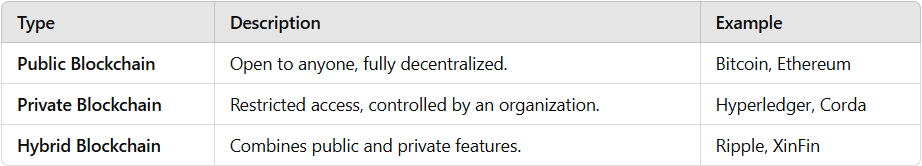
💡 Fact: Bitcoin’s blockchain is one of the most secure because of its massive decentralized network.
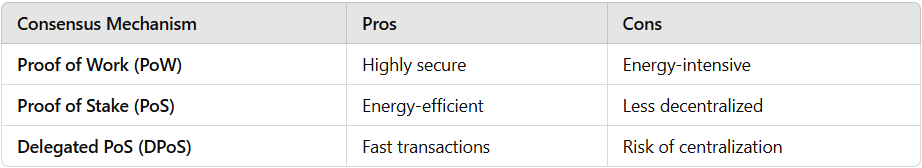
Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
To prevent fraud and ensure security, blockchains use consensus mechanisms to validate transactions.
🔹
Proof of Work (PoW)
–
Used by Bitcoin, miners solve complex puzzles to validate transactions.
🔹
Proof of Stake (PoS) – Used by Ethereum 2.0, validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold.
🔹
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
– Users vote for delegates to validate transactions.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain technology goes beyond cryptocurrencies. Here’s how it's being used in different industries:
📜
Smart Contracts
–
Self-executing contracts on Ethereum.
💳
Financial Services
– Faster cross-border payments using Ripple.
📦
Supply Chain Management
– Tracking goods from production to delivery (e.g., IBM Blockchain).
🏥
Healthcare
– Secure patient data sharing.
🎨
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens)
– Digital ownership of art and collectibles.
🚀 The Future of Blockchain: Blockchain is continuously evolving with advancements like Layer 2 solutions (Lightning Network), quantum-resistant cryptography, and AI-driven smart contracts.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we store and transfer data. It offers a trustless, secure, and transparent system that has the potential to reshape industries beyond cryptocurrency. Whether it’s finance, healthcare, or supply chains, blockchain is here to stay!

