Crypto vs. Traditional Finance - Key Differences Explained
Cryptocurrency is often compared to traditional finance (TradFi), but how do they really differ? This guide breaks down the key distinctions, covering decentralization, accessibility, security, and more.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Systems
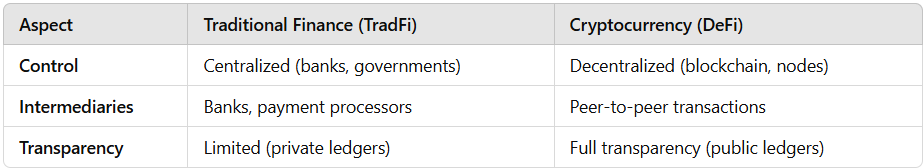
✔ Crypto eliminates intermediaries, allowing peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a bank.
❌ Traditional finance relies on trusted institutions, which can control transactions and impose fees.
Accessibility & Inclusion
Traditional finance requires users to have a bank account, which may not be available to everyone due to economic, political, or geographical barriers.
💡 Crypto is borderless and accessible to anyone with an internet connection, allowing unbanked populations to participate in global finance.
📌 Example: In countries with unstable economies, Bitcoin and stablecoins are used as alternatives to national currencies.
Security & Privacy
🔐 Traditional Finance Risks:
- Banks store personal data, making them a target for hackers.
- Government regulations can freeze accounts.
🛡 Crypto Security:
- Transactions are pseudonymous, increasing privacy.
- Security depends on private keys—losing your key means losing access to funds.
- Hacks are still possible, especially on exchanges.
⚠ Key Takeaway: Crypto enhances privacy but also puts the responsibility on the user to protect their assets.
💡 Fact: Bitcoin’s blockchain is one of the most secure because of its massive decentralized network.
Transaction Speed & Costs
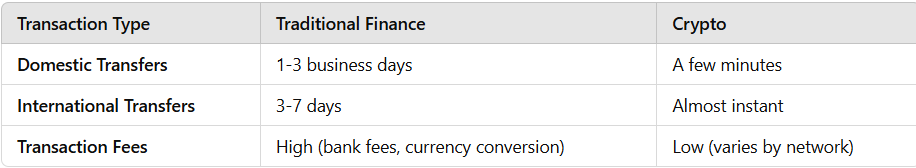
💳 TradFi Limitations: Cross-border transactions are slow and costly due to bank fees, intermediaries, and regulations.
⚡ Crypto Advantage: Transactions settle quickly with lower fees, especially with Layer 2 solutions like the Bitcoin Lightning Network.
Inflation & Monetary Policy
🔵 Traditional Finance:
- Governments control fiat money supply, often leading to inflation.
- Central banks can print more money, decreasing purchasing power.
🟠 Cryptocurrency:
- Bitcoin has a fixed supply (21 million coins), making it deflationary.
- Some cryptos have algorithmic supply control to manage inflation (e.g., Ethereum’s burn mechanism).
💡 Crypto is resistant to inflation because supply is often predetermined by code, unlike fiat currencies that can be devalued over time.
Investment & Wealth Growth
💰 Traditional Investments:
- Stocks, bonds, savings accounts, real estate.
- Regulated by governments, offering some protection.
🚀 Crypto Investments:
- Bitcoin, altcoins, staking, DeFi lending.
- High risk, high reward—crypto markets are more volatile than traditional stocks.
⚠ Key Risk: Crypto prices fluctuate rapidly, making it a risky but potentially lucrative investment.
Regulation & Legal Status
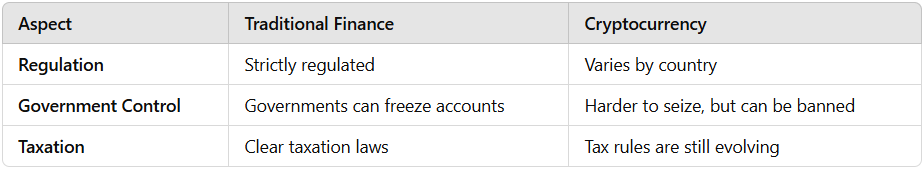
📌 Fact: Some governments ban crypto (e.g., China), while others regulate it (e.g., the U.S. and EU).
Conclusion:
Crypto and traditional finance both have advantages and limitations:
✔ Crypto offers
decentralization, transparency, and accessibility, but comes with security risks and volatility.
✔ Traditional finance provides
stability and regulation, but can be slow, costly, and restrictive.
💡 The Future? A mix of both—governments and banks are exploring Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and blockchain integration.

